Herniated discs in the neck (cervical), back (lumbar), or more rarely in the mid-back (thoracic) are illness caused by degeneration of structures called discs located between the spinal bones, due to various reasons such as trauma, heavy lifting, excess weight, aging, poor posture, and genetic predisposition. Following the degeneration of the annulus of the disc due to the mentioned reasons, the gel-like substance in the middle of the disc protrudes towards the spinal canal and results in compression of the spinal cord and nerves.
Symptoms vary depending on the location of the problem and the size of the herniation. If a herniated or degenerated disc does not compress any nerves, it may only cause neck or back pain. However, if it compresses a nerve in the neck region, symptoms such as shoulder and arm pain, numbness, and weakness in the hands and arms may occur. When there is pressure on the spinal cord, additional symptoms such as difficulty walking, leg cramps and spasms, coordination problems, and imbalance may arise in addition. In the case of the lower back, symptoms may include pain radiating to the hips, and legs, numbness, tingling, and weakness in the legs and feet, and in advanced stages, loss of bowel and bladder functions.
Diagnosis is made based on history, symptoms, neurological examination findings, and necessary diagnostic tests, which may include:
Non-surgical treatment methods can alleviate many complaints. Pain killers and muscle relaxants may be used. Restricting physical activity and using a cervical collar can support the spine and reduce pain and irritation. Trigger point injections may temporarily reduce pain. Algological interventions (epidural steroid injection, transforaminal injection, facet injection, etc.) may be beneficial in appropriate patients. Various physical therapy applications may alleviate patients' complaints in suitable cases. Conservative treatment options can be applied for up to six to eight weeks. If you experience numbness or weakness in your arm or leg during this treatment, or if your pain worsens, be sure to consult your physician again.
There are several treatment options available for treating disk herniations. The choice of surgical treatment depends on the characteristics of your disk disease, whether there is compression on the spinal cord or nerve roots, the location and size of this compression, your age, the status of any accompanying illnesses, and previous treatments applied for this condition.
If non-surgical treatment methods do not alleviate your symptoms, or if you experience progressing numbness, tingling, or weakness in your hands, arms, or legs, or if you have complaints such as difficulty walking and imbalance, surgical treatment may be required.
If you have sudden severe loss of strength, or if you have complaints of urinary or fecal incontinence along with numbness and tingling in your genital and anal area, you should undergo surgery as soon as possible.
There are various surgical treatment options available. You should decide on this option together with your phycisian based on the factors mentioned above. These options include percutaneous discectomy methods (laser discectomy, percutaneous automated discectomy, IDET, etc.), endoscopic discectomy, microdiscectomy, and conventional discectomy. Microdiscectomy is currently considered the gold standard surgical treatment method all over the world.
Piriformis syndrome is a neuromuscular condition that occurs when the piriformis muscle, located deep within the hip region, compresses or irritates the sciatic nerve passing nearby. While this muscle performs a critical function by enabling the external rotation of the leg, it exerts pressure on the sciatic nerve—the longest nerve in the body—in cases of […]
View in Detail
Basic Anatomy of The Spine and Spinal Cord The spine consists of 33 vertebrae. Seven of these bones are cervical vertebrae, 12 are thoracic vertebrae, and 5 are lumbar vertebrae. Five of them are fused to form the sacrum, and 4 are fused to form the coccyx, also known as the tailbone. The function of […]
View in Detail
Disc Herniation Herniated discs in the neck (cervical), back (lumbar), or more rarely in the mid-back (thoracic) are illness caused by degeneration of structures called discs located between the spinal bones, due to various reasons such as trauma, heavy lifting, excess weight, aging, poor posture, and genetic predisposition. Following the degeneration of the annulus of […]
View in Detail
Spondylolisthesis (Spinal Slippage) Spondylolisthesis, or spinal displacement (spinal slippage), is the displacement of one or more vertebrae in the spine that are normally aligned, due to various reasons. This displacement can occur forwards, backwards, to the right, or to the left, affecting the neck, back, or lower back. It can occur in a single vertebra […]
View in Detail
Spinal Stenosis (Narrowing of The Spinal Canal) Spinal stenosis, commonly known as "narrow canal," is a condition characterized by the narrowing of the spinal canal for various reasons, leading to pressure on the spinal cord and the nerves passing through it. This narrowing can occur at any level of the spine, including the neck (cervical), […]
View in Detail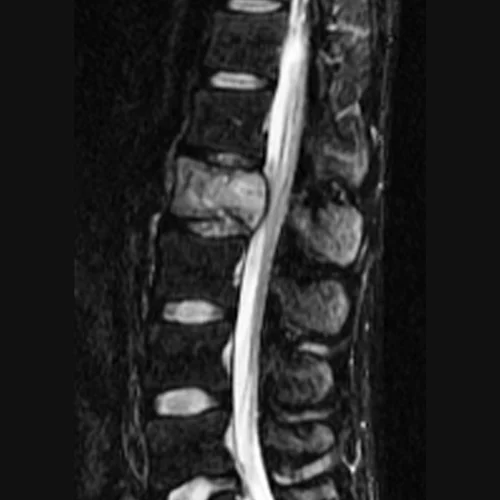
Spinal Tumors: Symptoms, Diagnostic Methods, and Current Treatment Approaches Spinal tumors are abnormal masses of cells that develop within the spinal canal or the bone structures (vertebrae) that make up the spine. These tumors can originate directly from the spine's own tissues (primary tumors) or occur when cancer from another part of the body (such […]
View in Detail
Carpal Tunnel Syndrome Carpal tunnel syndrome is a condition that occurs when the median nerve, one of the major nerves in the hand, is compressed and subjected to pressure within a structure called the carpal tunnel at the wrist level, due to various reasons. Causes include repetitive hand and wrist movements (computer use, playing musical […]
View in Detail
Cubital Tunnel Syndrome Cubital tunnel syndrome is a condition that occurs when the ulnar nerve, one of the three main nerves in the hand, becomes compressed or exposed to pressure at the elbow region. The nerve travels between two bony protrusions on the inner side of our elbow and passes through a structure called the […]
View in Detail
Thoracic outlet syndrome (TOS) is a complex condition that occurs as a result of the compression of nerves or blood vessels passing through the narrow space between the clavicle (collarbone) and the first rib, known as the thoracic outlet. This narrowing typically results from traumatic injuries, repetitive arm and shoulder movements, postural disorders, or anatomical […]
View in Detail
Basic Anatomy of Central Nervous System The nervous system is generally divided into the central nervous system and the peripheral nervous system. The central nervous system consists of the brain, brainstem, cerebellum, and spinal cord. The peripheral nervous system consists of spinal nerves originating from the spinal cord and the autonomic nervous system. MENINGES (BRAIN […]
View in Detail
Brain Tumors The causes of brain tumors are not fully understood, but risk factors include radiation exposure, genetic disorders, a family history of tumors, diseases that affect the immune system, stress, and exposure to various environmental carcinogens. It is thought that brain tumors occur as a result of damage or improper function of specific genes […]
View in Detail
Pituitary Tumor The pituitary gland is a vital endocrine gland located at the base of the brain in a small bony cavity called the "sella turcica" (Turkish saddle) and is widely known as the body's "conductor of the orchestra." Pituitary tumors are masses that arise from the abnormal and uncontrolled growth of cells within this […]
View in Detail
Chiari malformation (commonly known as Chiari syndrome) is a structural disorder characterized by the protrusion (herniation) of cerebellar tissue through the opening at the base of the skull (foramen magnum) into the spinal canal. Under normal conditions, the parts of the cerebellum should be located entirely within the skull; however, they are pushed downward due […]
View in Detail